Description
The project combines innovative and state-of-the-art technologies and methodologies. It will also integrate local and scientific knowledge, and open new learning spaces for stakeholders and researchers around agriculture management and related decisions. The project is designed towards increasing water efficiency of irrigation and profitability of the arid agricultural sector to improve its sustainability. This will be achieved by applying the latest technologies in remote, centralized, and frequent monitoring and operation of irrigation facilities. The results are technically more advanced, cost-effective and competitive irrigation process. The project will bring under the same umbrella all those who depend directly or indirectly on agricultural management and its improvement and could also be beneficiary of more sustainable management of water resources. Authorities, policymakers, scientists, agriculture, industry, market and more importantly, the citizens, will be engaged to ensure that it’s impacts, benefits and responsibilities for the future agro-environmental sustainability are shared across specific interests.
Natural aquifers, as well as other accessible water resources and technological components like wastewater and water treatment plants, pumping facilities, and water distribution networks will be considered jointly to devise sustainable management schemes meeting the demand at an acceptable cost for general society (users and activity sectors) and for the environment. This project will be designed to rely on relevant input data, channel them to appropriate models, and to communicate modeling results in an understandable, organized, and user-friendly form to its users. These findings will facilitate smart exploration of management options and informed decision-making by the responsible authorities/parties.
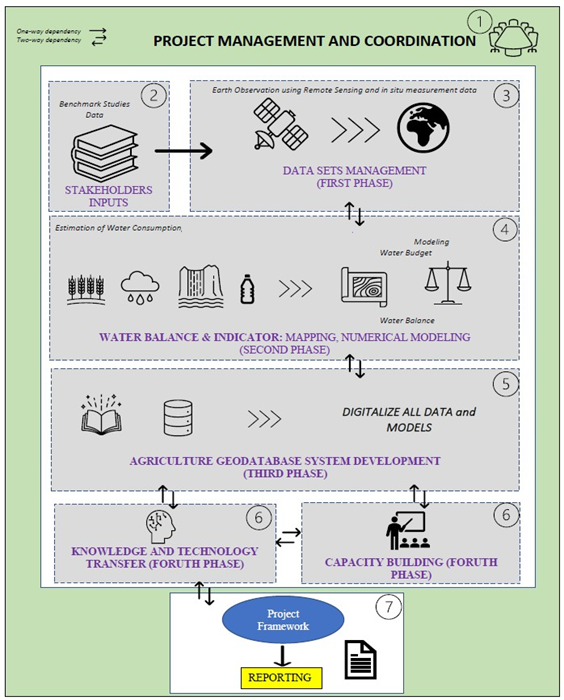
The starting point of the proposal concept (Figure 3.1) is the bidirectional relationship between water demand and consumption for agriculture. To study this complex decision-aided environment in a way that facilitates an internally consistent, realistic, and sustainable decision-making process, the project will develop an Agriculture Geodatabase Development System (AGDS) to assist integrated sustainable water management for agriculture in KSA. The AGSD will integrate the existing unified central geographic database available at SIO with the study results, such as water system’s main structural components, technologies and options, their characteristics, inputs and outputs depending on several factors, including type of crops, water consumption rates for each crop, water losses, etc.
AGSD is a module-based and scalable application with appropriate geo-spatial and relational databases. This application will contain all the results of this study which will be accessible by the users in the form of digital maps, reports and tables as appropriate. The user-friendly graphical user interface will ensure easy access, analysis and retrieval of information. The application will be developed using appropriate backend database and application program interfaces (APIs) for geo-spatial analyses. A user access control administration system will also be incorporated with the proposed application. This application will provide the option to enhance it by adding new modules in the future based on additional requirements. The methodology below will be conducted by KFUPM-RI to accomplish the objectives of the proposed study.